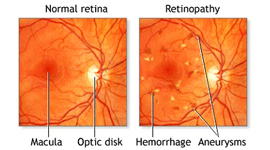
Proliferative Retinopathy affects up to 20% of all diabetics and can lead to very severe loss of sight resulting in blindness.
Diabetic Retinopathy
Regular eye check-up for Diabetic Retinopathy is a must for all diabetic patients. It is recommended that all diabetics should get their retina checked once every 6 months. It is quite common for a diabetic patient to have good vision without any realization of the changes happening in the retina. Early warning symptoms threatening and damaging the eyesight are rare in Diabetic retinopathy. These changes if left untreated could lead to sudden blindness due to bleeding.
Diagnosis:
Detailed retinal examination by the Doctor
Fundus Fluorescein Angiography or FFA, which is a specialized technique, is also used to get finer details of the retinal blood vessels. In FFA, a fluorescent dye is injected through a vein in the arm. As this dye travels through the bloodstream to reach the retinal blood vessels, photographs are taken in quick succession. These photographs capture the details of the dye leaking from the abnormal blood vessels. This helps in diagnosing the stage of diabetes and the subsequent managment.
OCT- an advanced retinal scan to detect retinal problems
Treatment for Diabetic retinopathy
Laser treatment or Laser Photocoagulation. It is the most common line of treatment in most sight threatening diabetic problems. It is very important to realize that laser treatment aims to save the existing sight level and not to make it better. Laser treatment is recommended to the patients who have swelling of the retina in the macular area or new blood vessel formation. Laser photocoagulation is used to seal the microanurysms that are leaking fluid into the retina. If new blood vessels are growing then more extensive laser treatment has to be carried out which is called the Pan Retinal Photocoagulation (PRP). PRP is carried out over two to three sittings spread over a few weeks. In most cases, laser treatment causes the new blood vessels to regress and the swelling to subside.
Some facts about laser treatment:
It is an outpatient procedure and does not involve stay in the hospital. It does not require an incision. It usually does not cause much discomfort. It can be repeated, if required. It prevents further loss of vision but does not restore the already lost vision.
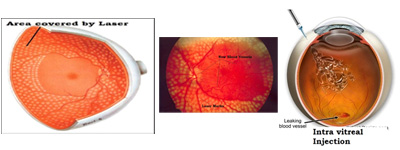
Intra vitreal injections:
An injection of Anti-VGF is given in to the eye in order to reduce the retinal swelling/ new blood vessels. In severe cases, injections may have to be repeated.
Vitrectomy and Vitreo Retinal Surgery
Sometimes the new blood vessels bleed into the gel like centre (vitreous) of the eye. This condition called vitreous hemorrhage & can lead to sudden loss of vision. If the vitreous hemorrhage is persistent , then a procedure called Vitrectomy is recommended. This is undertaken to remove the blood and scar tissue from the centre of the eye . Some Complicated diabetic retinal condition may require extensive surgeries known as Vitreoretinal surgery.